Obtaining a patent is a crucial step for inventors and businesses looking to protect their innovative ideas and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. If you wondered about how to obtain a patent, this post will walk you through the process, explain some key concepts, and discuss the policy behind patent protection.
The Purpose of Patents

Patents serve a vital role in promoting innovation and technological progress. By granting inventors exclusive rights to their creations for a limited time, the patent system incentivizes the development of new and useful inventions that benefit society. This policy encourages inventors to invest time and resources into research and development, knowing they can reap the rewards of their efforts.
How to Obtain a Patent: Key Concepts
Using a licensed patent attorney is critically important in obtaining a patent. However, before exploring how to obtain a patent, it’s important to understand the criteria for patentability, which every utility patent application must address. The four main requirements are:
- Patentable Subject Matter
- Novelty
- Non-obviousness
- Utility
Let’s explore these concepts in more detail.
Patentable Subject Matter
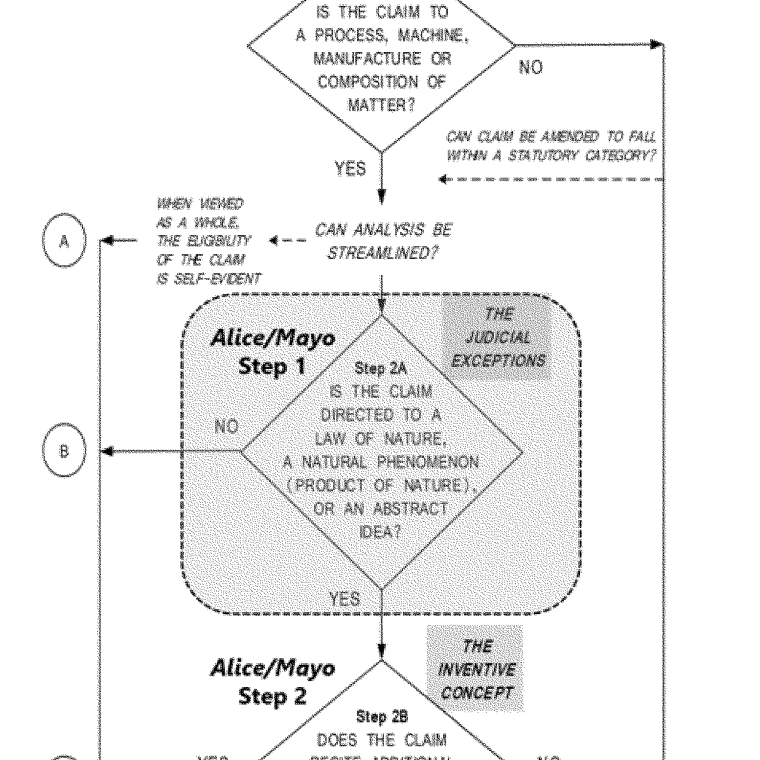
For an invention to be patentable, it must be an invention or discovery eligible for patent protection. Under 35 USC §101, this means that to be considered patentable subject matter, an invention must fall into one of four categories: processes, machines, manufactures, or compositions of matter. Additionally, the invention must not be directed to a judicial exception (such as abstract ideas, laws of nature, or natural phenomena) unless it includes additional elements that amount to significantly more than the judicial exception. For many inventions, this is not a high hurdle.
Novelty
For an invention to be patentable, it must be new or novel. This means that the invention should not have been publicly disclosed, used, or sold before the patent application is filed. Novelty is a fundamental requirement in how to obtain a patent, as it ensures that patents are only granted for truly innovative creations.
Non-obviousness
Non-obviousness is perhaps the most challenging requirement to meet when learning how to obtain a patent. An invention is considered non-obvious if it would not have been obvious to a person having ordinary skill in the relevant field of technology. This requirement prevents patents from being granted for minor, incremental improvements that would naturally occur to those working in the field.
Utility
The utility requirement ensures that the invention has a practical use or application. This is generally the easiest requirement to meet when figuring out how to obtain a patent, as most inventions are created to solve a specific problem or serve a particular purpose.
The Patent Process: An Overview
Now that we’ve covered the key concepts, let’s outline the general steps involved in how to obtain a patent:
- Conduct a patent search: Before filing an application, search existing patents and published applications to ensure your invention is novel.
- Determine the type of patent: Decide whether you need a utility patent, design patent, or plant patent.
- Prepare and file the application: Draft a detailed description of your invention and submit it to the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) along with the required fees.
- Examination: A patent examiner will review your application to determine if it meets the legal requirements for patentability.
- Respond to office actions: Address any objections or rejections raised by the patent examiner during the examination process.
- Obtain the patent: If your application is approved, pay the issue fee to receive your patent.
Prior Art and Its Importance
When determining how to obtain a patent, understanding the concept of prior art is crucial. Prior art refers to any publicly available information that predates the filing of a patent application. Patent examiners use prior art to assess both the novelty and non-obviousness of an invention.
Pertinent Prior Art
Pertinent prior art is a subset of prior art that is particularly relevant to the claimed invention. When evaluating the novelty of the invention, examiners often consider the pertinent prior art. In looking at the prior art, the invention must be new or novel. In addition, patent examiners often look at the pertinent prior art to determine if the invention meets the non-obviousness requirement.
The MPEP Test for Obviousness
The Manual of Patent Examining Procedure (MPEP), which is the Patent Examiner’s guide to examination of patents, provides guidance for patent examiners to assess obviousness. When learning how to obtain a patent, it’s essential to understand the obviousness test, as it can significantly impact the success of your application.
The MPEP test for obviousness, based on the Supreme Court’s decision in Graham v. John Deere Co., involves the following steps:
- Determine the scope and content of the prior art
- Ascertain the differences between the prior art and the claimed invention
- Resolve the level of ordinary skill in the pertinent art
- Evaluate any evidence of secondary considerations
If, after considering these factors, the patent examiner finds that the invention would have been obvious to a person of ordinary skill in the art, a presumption of obviousness is established.
Secondary Considerations in Obviousness Determinations
Secondary considerations that can also influence an examiner’s decision on obviousness. When learning how to obtain a patent, you should address the following factors to help overcome the presumption of obviousness:
- Commercial success
- Long-felt but unsolved needs
- Failure of others to solve the problem
- Unexpected results
- Skepticism of experts
- Copying by competitors
For example, if your product has achieved significant commercial success, it may indicate that the invention was not obvious to others in the field. This can be a powerful argument in favor of patentability when determining how to patent a product.
Navigating the Patent Process
Understanding how to patent a product is just the beginning. The patent application process can be complex and time-consuming. Here are some tips to help you navigate the process:
- Seek professional help: Contact our registered patent attorney to guide you through the intricacies of the patent process.
- Be thorough in your application: With the assistance of our patent attorney, prepare a patent applications.
- Respond Timely to the Patent Office: In response to the Patent Office questions or concerns, our patent attorney can negotiate with the Patent Examiner about why your invention is novel and non-obvious in light of new prior art.
- Be patient: The patent examination process is a long-term effort and can take several years.
- Consider international protection: If you plan to pursue international patent protection, explore international patent options like the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT).
Conclusion
Understanding the key concepts and policies behind patent protection is essential before embarking on the journey to obtain a patent. By grasping these fundamental principles, inventors and businesses can better navigate the complex process of patent application and increase their chances of successfully protecting their innovations.As you move forward with your patent application, remember that the process can be complex and time-consuming. Contact our patent attorney to obtain professional legal advice as your application travels through the intricacies of the patent process.