A Guide to Filing and Protecting AI Patents
The field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has seen explosive growth in recent years, and with it, a surge in AI patents filed at the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). From chatbots handling customer service inquiries to predictive analytics optimizing supply chain management, AI is transforming how businesses operate. AI is used in various fields such as science, education, healthcare, defense, e-commerce, finance, drug discovery, immunotherapy, automotive, finance, telecommunications and manufacturing – the list is too extensive and growing to fast to recite here. AI is no longer confined solely to the fields of mathematics, statistics and computer science.
The curent definition of AI is ‘the study and design of intelligent agents’, where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximise its chances of success. In general, there are three categories of AI inventions: inventions on AI, inventions using AI as a tool based on being trained on a set of data, which is typically based on a large language model. The third type of AI invention is AI-created inventions. Most AI inventions fall into the second category as the use of large language models becomes more prevalent. In most jurisdictions, the patentability of an invention in any one of these categories is considered similar to applying the general principles of patent eligibility, as the inventions are considered computer implemented (or mathematical methods).
The Rise of AI Patents
AI patents have experienced unprecedented growth in recent years. According to the USPTO’s Artificial Intelligence Patent Dataset (AIPD), the number of AI-related patent applications has grown exponentially since the early 2000s. This trend reflects the increasing importance of AI technologies across various industries and the need for robust intellectual property protection in this rapidly evolving field.
Patentable Subject Matter in AI Patents
Patentable subject matter eligibility for AI patents is a mess. The nature of AI involves algorithms, often rooted in mathematical concepts, which is typically prohibited under the existing patent laws, and as established by the Supreme Court’s Alice decision. This makes it difficult to demonstrate the practical application or technological improvement, two things the Alice decision required to overcome patent eligibility hurdles.
Common Types of AI Patents

Several types of AI patents are commonly filed and granted within TC2100, one of the technology centers focused on AI type of patents:
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Patents covering novel machine learning techniques, including deep learning, reinforcement learning, and ensemble methods.
- Natural Language Processing: AI patents related to text analysis, language translation, and speech recognition technologies.
- Computer Vision: Patents involving image and video analysis, object detection, and facial recognition systems.
- Predictive Analytics: AI patents covering algorithms for forecasting and decision-making in various domains.
- Neural Network Architectures: Patents on innovative neural network designs and training methodologies.
- AI Hardware: Patents related to specialized hardware for AI computations, such as neuromorphic chips.
- AI-Enabled Cybersecurity: Patents covering AI applications in network security and threat detection.
AI Mimicking Human and Data Processing
The lack of clear, universally applicable guidelines for AI patent eligibility adds another layer of complexity. While the USPTO has provided some guidance, significant ambiguity remains in how these guidelines should be interpreted for specific AI inventions. This is compounded by the fact that many AI techniques mimic human cognitive processes, potentially leading to rejections based on the invention being classified as a mental process that could be performed by a human. The data-centric nature of many AI inventions, often revolving around data processing and analysis, further blurs the line between patentable innovations and abstract ideas or mental processes.
Moreover, the intangible outputs often produced by AI systems pose a unique challenge in framing these innovations as concrete, patentable inventions. The complexity of AI systems can make it difficult to describe the invention in a way that clearly demonstrates its technical character and patentable elements. This challenge is exacerbated by varying interpretations among patent examiners, who may apply the eligibility guidelines differently, leading to inconsistent outcomes for similar AI inventions.
AI Policy Considerations
Underlying these technical and legal challenges is the broader debate about balancing innovation protection with public access. There’s an ongoing discussion about how to protect AI innovations through patents while ensuring that fundamental AI techniques remain available for public use and further innovation. This delicate balance adds another layer of consideration when determining the patentability of AI inventions.
AI Patent Evolutions
Given these multifaceted challenges, it becomes crucial for inventors and patent attorneys to approach AI patent applications with careful consideration and strategic thinking. Focusing on technical implementations, specific improvements to computer technology, and practical real-world applications can increase the likelihood of overcoming subject matter eligibility hurdles. The complexity of this landscape underscores the importance of experienced legal guidance in navigating the patenting process for AI innovations, ensuring that these cutting-edge technologies receive the protection they deserve while adhering to the evolving standards of patent law.
USPTO Patent Guidance
The USPTO has provided updated guidance on subject matter eligibility for AI inventions, addressing the challenges posed by the abstract nature of some AI technologies.
Based on the recent guidance, some key considerations for patentable subject matter in AI patents include:
- Practical Application: AI patents that demonstrate a practical application of the technology, solving a specific technical problem, are more likely to be considered patentable.
- Technological Improvement: Inventions that show a clear improvement to computer functionality or other technology are often viewed favorably.
- Specificity: AI patents with specific, non-generic implementations of AI techniques are more likely to overcome subject matter eligibility hurdles.
- Integration with Hardware: AI inventions that are closely integrated with hardware components often have a stronger case for patentability.
Tech Center 2100
In the USPTO, Technology Center 2100 handles computer architecture and software patents, where it focuses on computer reliability and control systems, memory access, computer architecture, databases and file management, software development, artificial intelligence (AI), and graphical user interfaces. Despite being home to various cutting-edge technologies critical for the modern tech economy, it receives the fewest patent applications as other computer and technology related tech centers like TC3700 and filings in TC2100 have been declining since 2013. Because it has fewer patents applications, it also receives far fewer Alice rejections than other software-heavy technology centers such as TC 3600 (41,476 vs. 89,642 for all time).
Recent Statistics on AI Patents
The growth of AI patents in TC2100 has been remarkable:
- As of 2024, AI-related patent applications in TC2100 have increased by over 300% compared to a decade ago.
- Approximately 25% of all patents granted in TC2100 now involve some form of AI technology.
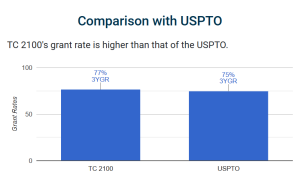
- With an overall allowance rate of 77% — which is higher than the USPTO average of 75% — TC 2100 is an ideal technology center for software applicants hoping to avoid the rigors of TC 3600
- Machine learning and computer vision patents account for nearly 60% of all AI patents granted in TC2100.
These statistics underscore the importance of AI patents and the increasing focus on strategic considerations when protecting AI innovations within the USPTO. As businesses and inventors seek to protect their AI innovations, understanding the legal landscape of AI patents, can be crucial.
The Importance of Experience in Filing AI Patents
Given the complex and rapidly evolving nature of AI technologies, working with an experienced patent attorney is crucial when filing AI patents. Here’s why:
- Navigating Subject Matter Eligibility: Experienced attorneys understand the nuances of subject matter eligibility for AI patents and can craft applications that meet the USPTO’s criteria.
- Technical Expertise: Patent attorneys with AI expertise can effectively communicate the technical aspects of your invention to patent examiners.
- Strategic Claim Drafting: Skilled attorneys can draft claims that provide broad protection while avoiding common pitfalls in AI patent applications.
- Prior Art Analysis: With the rapid pace of AI development, thorough prior art searches are crucial. Experienced attorneys have the resources and knowledge to conduct comprehensive searches.
- Responding to Office Actions: AI patents often face complex rejections. Experienced attorneys can craft persuasive arguments to overcome these objections.
- Future-Proofing: AI technologies evolve quickly. Skilled attorneys can draft patents with an eye towards future developments, ensuring long-term protection.
Conclusion: The Future of AI Patents
The landscape of AI patents is complex and ever-changing, with new challenges and opportunities emerging regularly. By understanding the types of AI patents commonly granted, the criteria for patentable subject matter, and the strategic considerations for filing AI patents, inventors and businesses can better position themselves to protect their AI innovations.
However, navigating this landscape requires more than just technical knowledge. Contacting an experienced patent attorney is invaluable in securing strong, enforceable AI patents. From crafting applications that meet subject matter eligibility requirements to strategically positioning your invention in the broader AI landscape, a skilled attorney can significantly enhance your chances of success.


